Choose Your Login Account
Thomson currently has two account systems - one for the website and CAD model downloads, and one for e-commerce. We understand that two logins is an inconvenience and are working to consolidate our systems into one login process. Until we’re able to consolidate the two logins, please follow these guidelines:
- Download CAD models
- Save and retrieve projects in LinearMotioneering® and MicronMotioneering® tools
- Access Distributor Extranet and all related resources
- Order directly from Thomson online (North America only)
- Authorized Thomson Distributors can view and order from quotes online (Global)
- View the shopping cart and look up prior direct orders

Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe
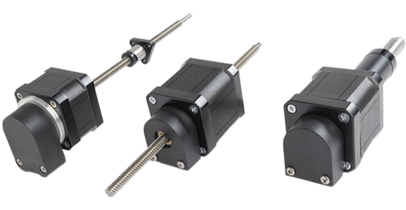
Thomson Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe kombinieren einen hybriden Schrittmotor mit einem präzisionsgefertigten Gewindetrieb zu einer kompakten Antriebslösung. Sie sind jetzt in drei Grundkonfigurationen erhältlich – angetriebene Spindel (MLS), angetriebene Mutter (MLN) und Aktuator-Version (MLA).
Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe - Standard
Aktuator (MLA)
Beim MLA handelt es sich um eine vollständig im Gehäuse untergebrachte Antriebslösung – zur Modell-Auswahl legen Sie einfach den Hub, den Verstellweg pro Schritt bzw. Umdrehung und den Präzisionsgrad fest.
Angetriebene Spindel (MLS)
Bei der MLS-Ausführung dreht der Schrittmotor eine Gewindespindel und bewegt damit eine an der Gewindemutter befestigte Last auf linearer Achse.
Angetriebene Mutter (MLN)
MLN-Einheiten arbeiten mit einer im Schrittmotorgehäuse drehenden Mutter. Die Bewegung erfolgt entweder durch Fixierung des Schrittmotors und Verfahren der an der Gewindemutter befestigten Last – oder durch Fixieren der Spindel und Verfahren einer am Motor befestigten Last.
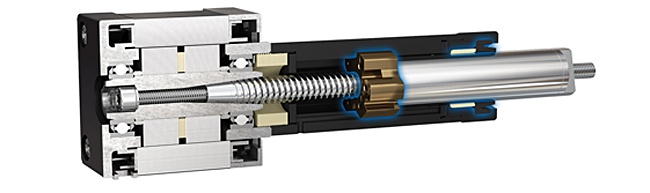
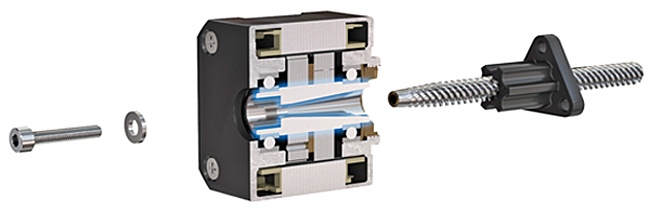
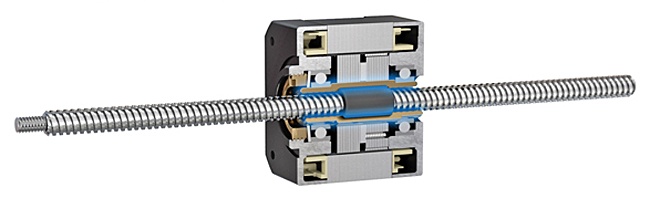
Rotary Encoders Available as a Standard Option

Rotary encoders deliver real-time information about position, speed and direction.
They can be seamlessly pre-assembled onto the backs of all three types of
Thomson stepper motor linear actuator assemblies as a standard option.
Please contact Thomson Customer Support for more details.
Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe - Sonderausführungen

Optimieren Sie Ihre Konstruktion mit einem speziell angepassten Schrittmotor-Linearantrieb.
Warum Thomson Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe?
Thomson hat drei Grundkonfigurationen im Programm – angetriebene Spindel (MLS), angetriebene Mutter (MLN) und Aktuator-Version (MLA). Mit ihrer offenen Architektur eignen sich die Motor-Gewindetriebe mit angetriebener Spindel bzw. Mutter, wenn eine externe Führung vorhanden oder eine hohe Flexibilität gefordert ist. Demgegenüber vereinfacht die geschlossene Aktuator-Ausführung das Design und kommt ohne externe Führungen aus.Sonderausführungen
Thomson arbeite regelmäßig mit Erstausrüstern (OEMs) aus aller Welt zusammen, um Probleme zu lösen, die Effizienz zu steigern und die Wertschöpfung für die Endkunden zu maximieren. Nutzen Sie unsere Technologie und Anwendungserfahrung, um jenseits von Standardlösungen die Anforderungen ihres nächsten Produkts zu erfüllen.Wo fangen Sie am besten an?
Thomson unterstützt Sie mit umfassenden Online-Quellen – ganz gleich, an welcher Stelle im Entscheidungsprozess Sie sich gerade befinden:VIDEO: Stepper Motor Linear Actuator Assembly Configurations
Precision lead screws can be combined with a stepper motor in a number of ways. At Thomson, we offer three configurations of stepper motor linear actuators to meet the various needs of our customers' applications. Learn more about them and discover which of them can benefit your linear motion designs.
VIDEO: What is a Stepper Motor and How is it Useful for Linear Motion?
Combined with a precision lead screw, the stepper motor is utilized in one of Thomson’s main product families – stepper motor linear actuators. This video takes a closer look at this motor, its main components, how they work, and why they are useful in linear motion applications in comparison to other types of motors.
VIDEO: Schrittmotor-Linearantrieb mit TaperLock
Dieses Video zeigt Ihnen die korrekte Wartung der Thomson Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe vor Ort. Die präzisionsgefertigten Einheiten kombinieren einen hybriden Schrittmotor und eine Leitspindel zu einem kompakten Modul. Das Ergebnis ist eine Lösung, die kleiner, stärker und effizienter ist als konkurrierende Technologien.
Technical Articles
-
Leveraging Stepper Motor Linear Actuator Configurability
When designers and integrators need simple, flexible and compact linear actuation, they often turn to stepper motor linear actuators (SMLAs). The high configurability of SMLAs is among their greatest virtues, but sorting through myriad configuration options to tailor the optimal solution for a particular application can be a challenge for even the most seasoned motion engineer. Understanding the unique capabilities and limitations of each type of SMLA will make it easier to take maximum advantage of their wide range of flexibility.
Mehr erfahren -
Einbau einer Verdrehschutzführung für Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe
Die Kombination von Gewindetrieben mit Schrittmotoren ist eine einfache und kosteneffizient Methode, präzise Linearbewegungen zu erzeugen. Für diese Präzision ist jedoch eine Vorrichtung als Verdrehschutz erforderlich, die entweder extern vom Anwender hinzugefügt oder bereits vom Gerätehersteller integriert werden muss. Um zu entscheiden, welche Variante sinnvoll ist, müssen Sie die Notwendigkeit eines Führungssystems analysieren und die Vor- und Nachteile der einzelnen Möglichkeiten gegeneinander abwägen.
Mehr erfahren -
Reduzieren Sie Ihre linearen Antriebsbaugruppen auf eine einzige Komponente – mit motorbetriebenen Linearantrieben.
Wenn es darum geht, Linearbewegungen in einer Maschine zu spezifizieren, stehen Systementwicklern viele Möglichkeiten zur Auswahl. Die richtige Wahl kann sich auf die Montagefreundlichkeit, den Platzbedarf und die Betriebskosten auswirken. Ein üblicher Antriebsmechanismus für eine lineare Bewegung ist eine Baugruppe aus Schrittmotor und einem extern gelagerten Gleitgewindetrieb. Eine einfachere und montagefreundlichere Lösung ist jedoch ein Antriebsmechanismus mit integrierter Führung und Abstützung, der dafür normalerweise benötigte externe Komponenten überflüssig macht und somit die Komplexität senkt.
Mehr erfahren
Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe – technische Daten (Zoll)
| S = Angetriebene Spindel (MLS), N = Angetriebene Mutter (MLN), A = Aktuator-Version (MLA) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubweg/Vollschritt [µZoll] / Full Step (μ in.) |
Steigung (mm) |
Steigungskennung (mm) |
Motor | |||||||||
| MLxX8 | MLx11 | MLx14, MLx17 | MLx23 | |||||||||
| Durchmesser-Kennung [Hundertstel-Zoll] | ||||||||||||
| 18 | 18 | 25 | 25 | 31 | 37 | 31 | 37 | 43 | 50 | |||
| 0.063² | 0.013 | 0013 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹³ | S¹³ | S,N¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹³ | |||
| 0.125² | 0.025 | 0025 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹³ | |||||
| 0.157 | 0.031 | 0031 | S,A | S,N,A | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||
| 0.165 | 0.033 | 0033 | S¹ | |||||||||
| 0.179 | 0.036 | 0036 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | ||||||||
| 0.200 | 0.040 | 0040 | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 0.209 | 0.042 | 0042 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹³ | S¹³ | S,N¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | ||||
| 0.250 | 0.050 | 0050 | S,A | S,N | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹³ | S¹³ | ||
| 0.313 | 0.063 | 0063 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S | S,N,A | S¹ | |||||
| 0.357 | 0.071 | 0071 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 0.394 | 0.079 | 0079 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||
| 0.417 | 0.083 | 0083 | S | S¹ | S,N | S,N,A¹ | ||||||
| 0.490 | 0.098 | 0098 | S¹ | |||||||||
| 0.500 | 0.100 | 0100 | S,A | S,N | S | S,N,A | S¹ | |||||
| 0.591 | 0.118 | 0118 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 0.625 | 0.125 | 0125 | S,A¹ | S,N¹ | S,A | S,N,A | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | |||
| 0.787 | 0.157 | 0157 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 0.833 | 0.167 | 0.167 | S | S | S,N | S,N,A | ||||||
| 0.960 | 0.192 | 0.192 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 1.000 | 0.200 | 0200 | S,A | S,N | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | |||
| 1.180 | 0.236 | 0236 | S¹ | |||||||||
| 1.250 | 0.250 | 0250 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S | S | S,N | S,N,A | S¹ | S¹ | ||
| 1.500 | 0.300 | 0.300 | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 1.665 | 0.333 | 0.333 | S,A¹³ | S,N¹³ | ||||||||
| 1.875 | 0.375 | 0.375 | S,A¹³ | S,N¹³ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||
| 2.000 | 0.400 | 0.400 | S,A | S,N | ||||||||
| 2.500 | 0.500 | 0500 | S,A¹³ | S,N¹³ | S,A | S,N,A | S | S | S,N | S,N,A | S¹ | S¹ |
| 3.750 | 0.750 | 0750 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | ||||||
| 4.000 | 0.800 | 0.800 | S¹³ | |||||||||
| 5.000 | 1.000 | 1000 | S³ | S³ | S,N³ | S,N,A³ | S¹³ | |||||
| 6.000 | 1.200 | 1.200 | S¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | ||||||||
| 7.500 | 1.500 | 1.500 | S¹³ | |||||||||
1. Einige Steigungen sind eventuell im Hochleistungs-Mutternwerkstoff, in Konfigurationen mit angetriebener Mutter (MLN) oder einigen spielfreien Muttern nicht verfügbar. Weitere Informationen erhalten Sie von Thomson.
2. Feingewindespindeln können deutlich geringere Tragzahlen im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Spindeln aufweisen.
3. Spindel in Präzisionsgenauigkeit (P) nicht verfügbar
Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe – technische Daten (metrisch)
| S = Angetriebene Spindel (MLS), N = Angetriebene Mutter (MLN), A = Aktuator-Version (MLA) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubweg/Vollschritt [µZoll] / Full Step (mm) |
Steigung (mm) |
Steigungskennung (mm) |
Motor | ||||||||
| MLxX8 | MLx11 | MLx14, MLx17 | MLx23 | ||||||||
| Durchmesser-Kennung | |||||||||||
| M04 | M04 | M06 | M06 | M08 | M10 | M08 | M10 | M12 | |||
| 3 | 0.6 | 006 (0024) | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | |||||||
| 5 | 1.0 | 010 (0039) | S | S,N | S,A | S,N,A | |||||
| 6 | 1.2 | 012 (0047) | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | |||||||
| 10 | 2.0 | 020 (0079) | S | S | S,N | S,N,A | S¹ | ||||
| 15 | 3.0 | 030 (0118) | S | S,N,A | S¹ | ||||||
| 20 | 4.0 | 040 (0157) | S | S,N | S | S,N | S¹ | ||||
| 25 | 5.0 | 050 (0197) | S | S,N,A | |||||||
| 30 | 6.0 | 060 (0236) | S,A | S,N,A | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | ||||
| 40 | 8.0 | 080 (0315) | S³ | S,N³ | S | S,N | |||||
| 50 | 10.0 | 100 (0394) | S | S,N,A | S¹ | ||||||
| 60 | 12.0 | 120 (0472) | S,A | S,N,A | S | S¹ | S,N | S,N,A¹ | |||
| 75 | 15.0 | 150 (0591) | S¹ | ||||||||
| 80 | 16.0 | 160 (0630) | S¹ | ||||||||
| 90 | 18.0 | 180 (0709) | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | |||||||
| 100 | 20.0 | 200 (0787) | S³ | S | S,N³ | S,N,A | |||||
| 125 | 25.0 | 250 (0984) | S¹³ | ||||||||
| 175 | 35.0 | 350 (1378) | S¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | |||||||
| 225 | 45.0 | 450 (1772) | S¹³ | ||||||||
1. Einige Steigungen sind eventuell im Hochleistungs-Mutternwerkstoff, in Konfigurationen mit angetriebener Mutter (MLN) oder einigen spielfreien Muttern nicht verfügbar. Weitere Informationen erhalten Sie von Thomson.
2. Steigungskennung für MLA in Klammern.
3. Spindel in Präzisionsgenauigkeit (P) nicht verfügbar
Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe – Produkthighlights
- Erhöhte Drehmomentdichte
- Erhöhter Wirkungsgrad
- Angetriebene Spindel oder angetriebene Mutter
- Spindel-Sonderausführungen nach Kundenvorgabe erhältlich
- TaperLock-Vorteil
- Minimierte Geräuschentwicklung
- Zoll- oder metrische Größen verfügbar
Anwendungsbeispiele:
- Medizinische Geräte
- X-Y-Stufen
- 3D-Drucker
- HLK-Regelventile
- Pipettiervorrichtungen
- CNC-Maschinen
- Fluid-/Injektionspumpen
Broschüren
| Stepper Motor Specification Change Notice | 362 KB | |
| Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe | 11795 KB | |
| Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe | 4302 KB | |
| Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe | 4294 KB | |
| Stepper Motor Linear Actuators | 3629 KB | |
| Schrittmotor-Linearantriebe | 4435 KB | |
| Miniature Components and Systems | 6871 KB | |
| Miniature Components and Systems | 6862 KB |
Handbücher
Choose Your CAD Model:
MLA

MLS

MLN

To download the models below, you will need to sign in.
To provide better service to you on our websites, we and our service providers use cookies to collect your personal data when you browse. For information about our use of cookies and how to decline them or turn them off please read our cookie policy [available here].