Choose Your Login Account
Thomson currently has two account systems - one for the website and CAD model downloads, and one for e-commerce. We understand that two logins is an inconvenience and are working to consolidate our systems into one login process. Until we’re able to consolidate the two logins, please follow these guidelines:
- Download CAD models
- Save and retrieve projects in LinearMotioneering® and MicronMotioneering® tools
- Access Distributor Extranet and all related resources
- Order directly from Thomson online (North America only)
- Authorized Thomson Distributors can view and order from quotes online (Global)
- View the shopping cart and look up prior direct orders

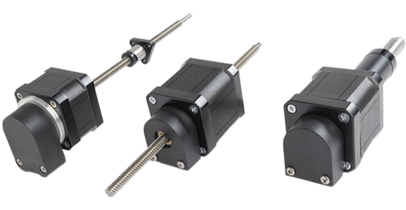
Attuatore lineare con motore passo-passo
Gli attuatori lineari con motore passo-passo di Thomson combinano un motore passo-passo ibrido con una madrevite di precisione in un unico involucro compatto. Oggi vengono proposti in tre configurazioni di base: vite rotante (MLS), chiocciola (MLN) e attuatore (MLA).
Attuatori lineari con motore passo-passo standard
Attuatore (MLA)
Gli MLA sono completamente racchiusi nell’alloggiamento in cui viene garantito il motion desiderato. Scegliere il modello adatto è semplice: è sufficiente stabilire la lunghezza della corsa, la corsa lineare per passo o rotazione, e il livello di precisione.
Vite rotante (MLS)
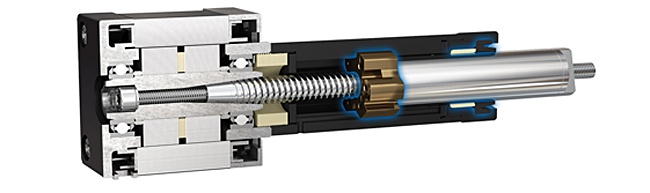
I gruppi MLS si attivano mediante il motore passo-passo che fa girare una madrevite e trasferisce un carico fissato alla chiocciola.
Chiocciola (MLN)
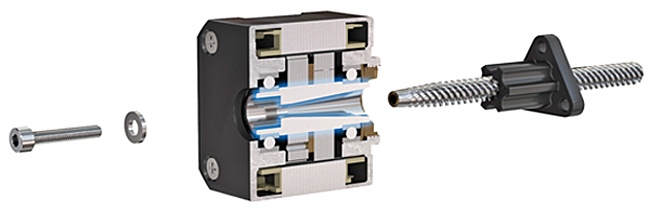
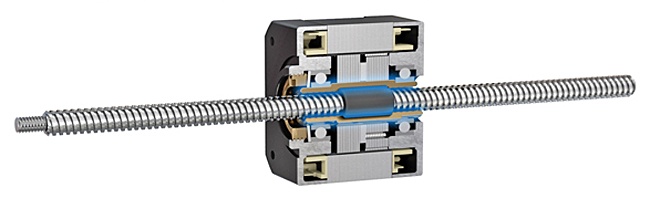
I gruppi MLN si attivano facendo ruotare una chiocciola nel corpo motore. Si ottiene il movimento inibendo il motore e trasferendo un carico collegato alla madrevite o inibendo la madrevite e trasferendo un carico collegato al motore passo-passo.
Rotary Encoders Available as a Standard Option

Rotary encoders deliver real-time information about position, speed and direction.
They can be seamlessly pre-assembled onto the backs of all three types of
Thomson stepper motor linear actuator assemblies as a standard option.
Please contact Thomson Customer Support for more details.
Options d'actionneur linéaire à moteur pas à pas personnalisé

Optimisez votre conception avec une solution personnalisée d'actionneur linéaire à moteur pas à pas.
Perché gli attuatori lineari con motore passo-passo di Thomson?
Oggi vengono proposti in tre configurazioni di base: vite rotante (MLS), chiocciola (MLN) e attuatore (MLA). L’architettura aperta delle madreviti motorizzate con vite rotante e chiocciola è la risposta per applicazioni in cui è presente una guida esterna o è richiesto un elevato livello di flessibilità di progettazione, mentre il gruppo chiuso dell’attuatore con madrevite motorizzata è ideale per semplificare ulteriormente il processo di progettazione ed eliminare la guida esterna.Opzioni di personalizzazione
Thomson lavora sempre in collaborazione con i produttori OEM di tutto il mondo, al fine di risolvere i problemi, migliorare l’efficienza e aumentare il valore che forniamo ai nostri clienti. La nostra esperienza in ambito tecnologico e applicativo può essere sfruttata per aiutarti ad andare oltre i prodotti standard e soddisfare le specifiche esigenze del tuo prossimo prodotto.Da dove si può cominciare?
Thomson fornisce un'ampia gamma di risorse in linea per assisterti in qualsiasi fase del processo di acquisto:VIDEO: Stepper Motor Linear Actuator Assembly Configurations
Precision lead screws can be combined with a stepper motor in a number of ways. At Thomson, we offer three configurations of stepper motor linear actuators to meet the various needs of our customers' applications. Learn more about them and discover which of them can benefit your linear motion designs.
VIDEO: What is a Stepper Motor and How is it Useful for Linear Motion?
Combined with a precision lead screw, the stepper motor is utilized in one of Thomson’s main product families – stepper motor linear actuators. This video takes a closer look at this motor, its main components, how they work, and why they are useful in linear motion applications in comparison to other types of motors.
VIDEO: Attuatore lineare con motore passo-passo con Taper-Lock
Scoprite come procedere a una manutenzione corretta sul posto dell’attuatore lineare con motore passo-passo Thomson. Le unità sviluppate con tecnologia di precisione combinano un motore passo-passo ibrido con una madrevite di precisione in un unico involucro compatto, per fornire indubbi vantaggi grazie a una soluzione più piccola, più potente e più efficiente di tecnologie alternative.
Technical Articles
-
Leveraging Stepper Motor Linear Actuator Configurability
When designers and integrators need simple, flexible and compact linear actuation, they often turn to stepper motor linear actuators (SMLAs). The high configurability of SMLAs is among their greatest virtues, but sorting through myriad configuration options to tailor the optimal solution for a particular application can be a challenge for even the most seasoned motion engineer. Understanding the unique capabilities and limitations of each type of SMLA will make it easier to take maximum advantage of their wide range of flexibility.
Ulteriori informazioni -
Implementazione di una guida antirotazione per gli attuatori lineari con motore passo-passo
L'integrazione di madreviti con motori passo-passo è un metodo semplice ed economico per ottenere un movimento lineare preciso. Per ottenere tale precisione occorre però una guida antirotazione, che deve essere aggiunta dall'esterno dall'utente e inserita nella progettazione dal costruttore. Per stabilire l'opzione migliore è necessaria un'analisi del fabbisogno di un sistema di guida e una ponderazione di vantaggi e svantaggi di ciascun approccio.
Ulteriori informazioni -
Riduci i gruppi di movimento lineare a un singolo componente con gli attuatori a madrevite motorizzata
Quando si tratta di decidere la soluzione di movimento lineare per una macchina, i progettisti di sistemi hanno ampie possibilità di scelta. La scelta giusta può influire sulla semplicità di installazione, sugli ingombri e sul costo di esercizio. Un comune meccanismo di azionamento per il movimento lineare è un gruppo costituito da motore passo-passo con madrevite supportata esternamente. Un approccio più semplice e facile da installare è tuttavia la selezione di un meccanismo di azionamento con guida e supporto integrati, che elimina quindi la necessità di componenti esterni che normalmente gestirebbero queste funzioni e la complessità che ne deriva.
Ulteriori informazioni
Specifiche degli attuatori lineari con motore passo-passo (unità in pollici):
| S = Vite rotante (MLS), N = Chiocciola (MLN), A = Attuatore (MLA) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corsa lineare / passo completo (μ pollici) / Full Step (μ in.) |
Avanzamento (mm) |
Designazione avanzamento (mm) |
Motore | |||||||||
| MLxX8 | MLx11 | MLx14, MLx17 | MLx23 | |||||||||
| Designazione diametro [diametro in centesimi di diametro di pollici] | ||||||||||||
| 18 | 18 | 25 | 25 | 31 | 37 | 31 | 37 | 43 | 50 | |||
| 0.063² | 0.013 | 0013 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹³ | S¹³ | S,N¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹³ | |||
| 0.125² | 0.025 | 0025 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹³ | |||||
| 0.157 | 0.031 | 0031 | S,A | S,N,A | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||
| 0.165 | 0.033 | 0033 | S¹ | |||||||||
| 0.179 | 0.036 | 0036 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | ||||||||
| 0.200 | 0.040 | 0040 | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 0.209 | 0.042 | 0042 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹³ | S¹³ | S,N¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | ||||
| 0.250 | 0.050 | 0050 | S,A | S,N | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹³ | S¹³ | ||
| 0.313 | 0.063 | 0063 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S | S,N,A | S¹ | |||||
| 0.357 | 0.071 | 0071 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 0.394 | 0.079 | 0079 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||
| 0.417 | 0.083 | 0083 | S | S¹ | S,N | S,N,A¹ | ||||||
| 0.490 | 0.098 | 0098 | S¹ | |||||||||
| 0.500 | 0.100 | 0100 | S,A | S,N | S | S,N,A | S¹ | |||||
| 0.591 | 0.118 | 0118 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 0.625 | 0.125 | 0125 | S,A¹ | S,N¹ | S,A | S,N,A | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | |||
| 0.787 | 0.157 | 0157 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 0.833 | 0.167 | 0.167 | S | S | S,N | S,N,A | ||||||
| 0.960 | 0.192 | 0.192 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 1.000 | 0.200 | 0200 | S,A | S,N | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | |||
| 1.180 | 0.236 | 0236 | S¹ | |||||||||
| 1.250 | 0.250 | 0250 | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | S | S | S,N | S,N,A | S¹ | S¹ | ||
| 1.500 | 0.300 | 0.300 | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||||
| 1.665 | 0.333 | 0.333 | S,A¹³ | S,N¹³ | ||||||||
| 1.875 | 0.375 | 0.375 | S,A¹³ | S,N¹³ | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | ||||||
| 2.000 | 0.400 | 0.400 | S,A | S,N | ||||||||
| 2.500 | 0.500 | 0500 | S,A¹³ | S,N¹³ | S,A | S,N,A | S | S | S,N | S,N,A | S¹ | S¹ |
| 3.750 | 0.750 | 0750 | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | S¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | ||||||
| 4.000 | 0.800 | 0.800 | S¹³ | |||||||||
| 5.000 | 1.000 | 1000 | S³ | S³ | S,N³ | S,N,A³ | S¹³ | |||||
| 6.000 | 1.200 | 1.200 | S¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | ||||||||
| 7.500 | 1.500 | 1.500 | S¹³ | |||||||||
1. È possibile che alcuni avanzamenti non siano disponibili in materiale per chiocciole ad alte prestazioni, configurazioni di chiocciola (MLN) o per alcune chiocciole senza gioco. Per maggiori dettagli, contattare Thomson.
2. Madreviti a passo fine possono presentare capacità di carico notevolmente inferiori rispetto alle classiche madreviti.
3. Madreviti non disponibili nell’accuratezza del grado di precisione (P)
Specifiche degli attuatori lineari con motore passo (unità di misura metriche):
| S = Vite rotante (MLS), N = Chiocciola (MLN), A = Attuatore (MLA) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corsa lineare / passo completo (μ pollici) / Full Step (mm) |
Avanzamento (mm) |
Designazione avanzamento (mm) |
Motore | ||||||||
| MLxX8 | MLx11 | MLx14, MLx17 | MLx23 | ||||||||
| Designazione diametro | |||||||||||
| M04 | M04 | M06 | M06 | M08 | M10 | M08 | M10 | M12 | |||
| 3 | 0.6 | 006 (0024) | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | |||||||
| 5 | 1.0 | 010 (0039) | S | S,N | S,A | S,N,A | |||||
| 6 | 1.2 | 012 (0047) | S,A¹ | S,N,A¹ | |||||||
| 10 | 2.0 | 020 (0079) | S | S | S,N | S,N,A | S¹ | ||||
| 15 | 3.0 | 030 (0118) | S | S,N,A | S¹ | ||||||
| 20 | 4.0 | 040 (0157) | S | S,N | S | S,N | S¹ | ||||
| 25 | 5.0 | 050 (0197) | S | S,N,A | |||||||
| 30 | 6.0 | 060 (0236) | S,A | S,N,A | S¹ | S,N,A¹ | S¹ | ||||
| 40 | 8.0 | 080 (0315) | S³ | S,N³ | S | S,N | |||||
| 50 | 10.0 | 100 (0394) | S | S,N,A | S¹ | ||||||
| 60 | 12.0 | 120 (0472) | S,A | S,N,A | S | S¹ | S,N | S,N,A¹ | |||
| 75 | 15.0 | 150 (0591) | S¹ | ||||||||
| 80 | 16.0 | 160 (0630) | S¹ | ||||||||
| 90 | 18.0 | 180 (0709) | S,A¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | |||||||
| 100 | 20.0 | 200 (0787) | S³ | S | S,N³ | S,N,A | |||||
| 125 | 25.0 | 250 (0984) | S¹³ | ||||||||
| 175 | 35.0 | 350 (1378) | S¹³ | S,N,A¹³ | |||||||
| 225 | 45.0 | 450 (1772) | S¹³ | ||||||||
1. È possibile che alcuni avanzamenti non siano disponibili in materiale per chiocciole ad alte prestazioni, configurazioni di chiocciola (MLN) o per alcune chiocciole senza gioco. Per maggiori dettagli, contattare Thomson.
2. Tra parentesi sono riportate le designazioni avanzamenti per MLA.
3. Madreviti non disponibili nell’accuratezza del grado di precisione (P)
Caratteristiche principali degli attuatori lineari con motore passo-passo
- Maggiore densità di coppia
- Efficienza migliorata
- Chiocciola o vite rotante
- Taglie/passi personalizzati disponibili
- Tecnologia taper-lock
- Rumore ridotto
- Versioni metriche o in pollici
Esempi applicativi
- Dispositivi medici
- Piastre X-Y
- Stampa in 3D
- Valvole di controllo HVAC
- Dispositivi di pipettaggio
- Macchine CNC
- Pompe per liquidi/a siringa
Opuscoli
Manuali
Scegli il tuo modello CAD:
MLA

MLS

MLN

Per scaricare i modelli qui sotto, occorre registrarsi.
To provide better service to you on our websites, we and our service providers use cookies to collect your personal data when you browse. For information about our use of cookies and how to decline them or turn them off please read our cookie policy [available here].